Choosing the right healthcare provider for your children is a crucial decision that every parent faces.
Pediatricians and family doctors both provide comprehensive medical care, but their scopes of practice and patient age ranges differ significantly.
While pediatricians are dedicated to caring for children from infancy through adolescence, family doctors manage health care for individuals across all life stages, including children.
This distinction is important because the developmental needs and medical issues of children can be quite different from those of adults.
Key Takeaways
- Pediatricians specialize in child healthcare; family doctors treat all ages.
- Choosing depends on family health needs and preferences for care continuity.
- Both types of doctors are equipped to provide high-quality medical care.
The Roles
In choosing between a pediatrician and a family doctor for your family’s healthcare needs, it is critical to understand their respective roles. Each type of healthcare provider brings distinct expertise and capabilities that are tailored to different patient populations.
The proper selection is crucial. You need a good one so it can prescribe the right antibiotic, evaluate the condition accurately, and many other reasons.
Primary Care Responsibilities
Both pediatricians and family doctors share the common goal of providing primary care. They are the first healthcare professionals patients consult for health issues. Their responsibilities include conducting routine checkups, and immunizations, diagnosing various conditions, and managing chronic illnesses.
Pediatrician’s Focus
A pediatrician specializes in the physical, behavioral, and mental health care of children from birth to adolescence. They are trained to understand children’s health needs, growth milestones, and childhood illnesses. Pediatricians often act as a guide for parents regarding preventive health care and developmental issues relevant to each stage of a child’s growth.
Family Doctor’s Range
Family doctors, also known as family physicians, provide comprehensive care to patients of all ages, from infants to the elderly. Their broad training includes pediatrics, but also encompasses internal medicine, obstetrics, and geriatrics. They are uniquely positioned to develop long-term relationships with entire families, often treating multiple generations within the same family.
Training and Qualifications
When choosing between a pediatrician and a family doctor, it’s important to consider their distinct training and qualifications. These differences equip them to handle the unique health needs of specific age groups.
Pediatricians’ Specialized Training
Pediatricians focus exclusively on the health care of infants, children, and adolescents. They undergo a three-year residency in pediatrics after completing medical school, honing skills to tackle health issues prevalent among the younger population. Their extensive training covers childhood diseases, growth and development, and preventive health care. Pediatricians may see patients up to 21 years old, although some extend their care to those up to 24 years old.
Family Doctors’ Broad Training
Family doctors, also known as family physicians, are trained to provide comprehensive health care for individuals across all ages—from newborns to geriatric patients. They complete a three-year residency program in family medicine, which prepares them to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions. Family doctors are well-versed in adult and pediatric medicine, gynecology, and geriatrics, making them a one-stop resource for families seeking continuous care throughout their lives.
Choosing the Right Care Provider for Your Family
When deciding between a pediatrician and a family doctor, it’s crucial to assess your child’s healthcare needs and your family’s preferences. Here are some specific factors to consider for each option to make an informed decision.
Considerations for Pediatrician

- Training: Pediatricians are specialized in pediatric medicine, meaning they have comprehensive training focused exclusively on children’s health, development, and diseases.
- Patient Age Range: Typically, pediatricians care for patients from birth to 18 years. Some may extend care to young adults up to 21 years old.
Considerations for Family Doctor
- Patient Demographics: A family doctor is trained to treat a wide range of patients, from infants to seniors, thereby providing continuity of care that can span generations.
- Scope of Practice: Family doctors diagnose and treat a broad array of ailments and can be particularly beneficial for families seeking comprehensive care for all members in a single practice.
Evaluating Your Family’s Needs
- Health History: Consider your family’s overall health history. A family doctor might be ideal if you want a single healthcare provider knowledgeable about the family’s medical background.
- Convenience: Think about logistics. If the idea of having a single location for all family members’ medical care is appealing, a family doctor may be a more convenient option.
By weighing these considerations, families can better choose a healthcare provider that aligns with their specific health needs and preferences.
Common Conditions and Treatments
In the realm of primary care, pediatricians and family doctors diagnose and manage a diverse range of health issues across different age groups.
Pediatric Health Concerns

Pediatricians specifically focus on conditions prevalent in infants, children, and teenagers. They are experts in growth and development milestones, routine childhood vaccinations, and the management of common childhood illnesses such as ear infections, asthma, and skin conditions like eczema.
They also play a critical role in the early detection and treatment of more severe health issues, including congenital disorders and developmental delays. Pediatricians routinely address the healthcare needs of children with chronic conditions, tailoring treatments to the intricacies of a child’s evolving physiology.
Family Health Services
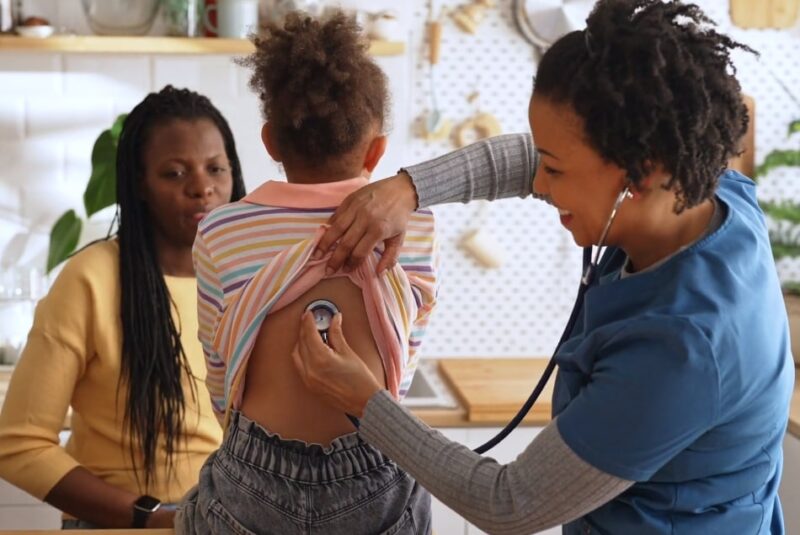

Family doctors provide comprehensive care that covers all life stages. They possess a broad knowledge base that allows them to treat a vast multitude of conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease, as well as provide preventative care and cancer screenings for adults.
For children, they manage similar acute conditions as pediatricians, like influenza and strep throat. Additionally, they can also offer continuous care for chronic issues in both adults and children, ensuring a seamless transition into adult health care for adolescents.
Long-Term Healthcare Relationships
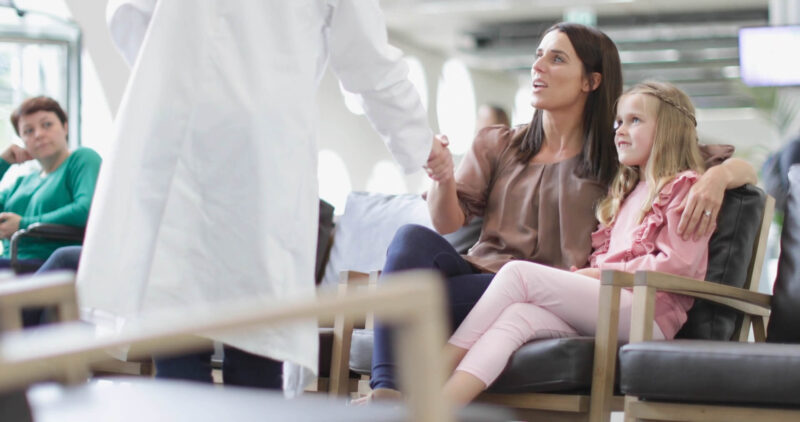

Building a long-term healthcare relationship with your healthcare provider—whether it’s with a pediatrician or a family doctor—ensures comprehensive and consistent medical support throughout different life stages.
Continuity of Care in Pediatrics
Pediatricians often establish an early and consistent connection with their patients from birth to late adolescence. This focused care is crucial because it allows the pediatrician to monitor the child’s developmental milestones, immunizations, and any health concerns that arise in their formative years.
Continuity of Care in Family Medicine
Family medicine doctors provide a broad spectrum of care that evolves with individuals and families over time, from childhood through senior years. The benefit for patients is the doctor’s broad expertise in treating a range of conditions and the convenience of family-centric care addressing the needs of all family members.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should be considered when choosing between a pediatrician and a family doctor for a newborn?
When selecting healthcare for a newborn, parents should consider the specific health needs of their child, the doctor’s specialization in age-related health issues, and the comfort and rapport the family has with the practitioner. Pediatricians exclusively treat infants through adolescents, offering focused care for this age group.
At what age is it typically appropriate to transition a child from a pediatrician to a family doctor?
The transition from a pediatrician to a family doctor usually occurs when a patient becomes a young adult, generally around 18 years of age. Some pediatricians may see patients until age 21, accommodating the transition to adulthood.
Are there differences in the training and scope of practice between pediatricians and family doctors?
Pediatricians undergo specialized training in treating children from birth to adolescence, covering a range of childhood illnesses and developmental issues. Family doctors are trained to provide comprehensive care to patients of all ages, which includes children, adults, and the elderly.
How can one find a pediatric family doctor in their local area?
One can find a pediatric family doctor by seeking referrals from their current pediatrician, using online resources and directories, or by consulting with local medical institutions and insurance providers to identify practitioners who offer family medicine with a focus on pediatrics in their area.
What are the pros and cons of having a single family doctor for all family members, including children?
Having a single family doctor means establishing a singular, long-term medical relationship that can oversee and coordinate the health of all family members. However, it may lack the specialized pediatric care that a dedicated pediatrician provides for children and the tailored care that certain age groups or health conditions might require.
How does the approach to healthcare differ between pediatricians and family medicine practitioners?
Pediatricians focus on the physical, mental, and behavioral health aspects unique to children and teens, adopting an approach tailored to these age groups. Family medicine practitioners offer a broader healthcare approach that addresses the needs of an entire family, from infants to seniors, across all health concerns.
Conclusion
Choosing between a pediatrician and a family doctor for your family’s healthcare needs is a significant decision that depends on various factors, including the specific health needs of your children, the desire for continuity of care, and personal preferences for healthcare provider relationships.
Pediatricians offer specialized care focused on the unique developmental and health needs of children and adolescents, while family doctors provide comprehensive care across all life stages, allowing for a holistic approach to family health.

